6 Causes of No Period After Planovar(a combined oral contraceptive pill ) & Solutions: Could You Be Pregnant?
Supervising Doctor

“I finished my Planovar(a combined oral contraceptive pill ) Pills my period still hasn’t come… Is this normal? Could I be pregnant?”
When you’ve finished your prescribed course of Planovar(a combined oral contraceptive pill ) Pills and your period is late beyond the expected date, it’s completely natural to feel anxious. This concern becomes even more stressful when you have important work commitments, travel plans, or other significant events where unpredictable timing could cause complications.
This comprehensive article addresses the following common concerns:
- Why hasn’t my period started even days after finishing Planovar(a combined oral contraceptive pill )?
- When should I take a pregnancy test for accurate results?
- What symptoms warrant immediate medical consultation?
Combined oral contraceptive pills are prescribed as hormone therapy for menstrual cycle regulation and various treatment purposes, but post-treatment bodily responses vary significantly between individuals. This article provides medically-informed explanations about the causes of delayed periods and appropriate management strategies in an easily understandable format.
Personal care Clinic offers specialized gynecological consultations, including online telemedicine services, for women experiencing menstrual irregularities and hormonal imbalances. If you’re seeking personalized medical advice for your specific situation, we encourage you to schedule a consultation with our experienced healthcare professionals.

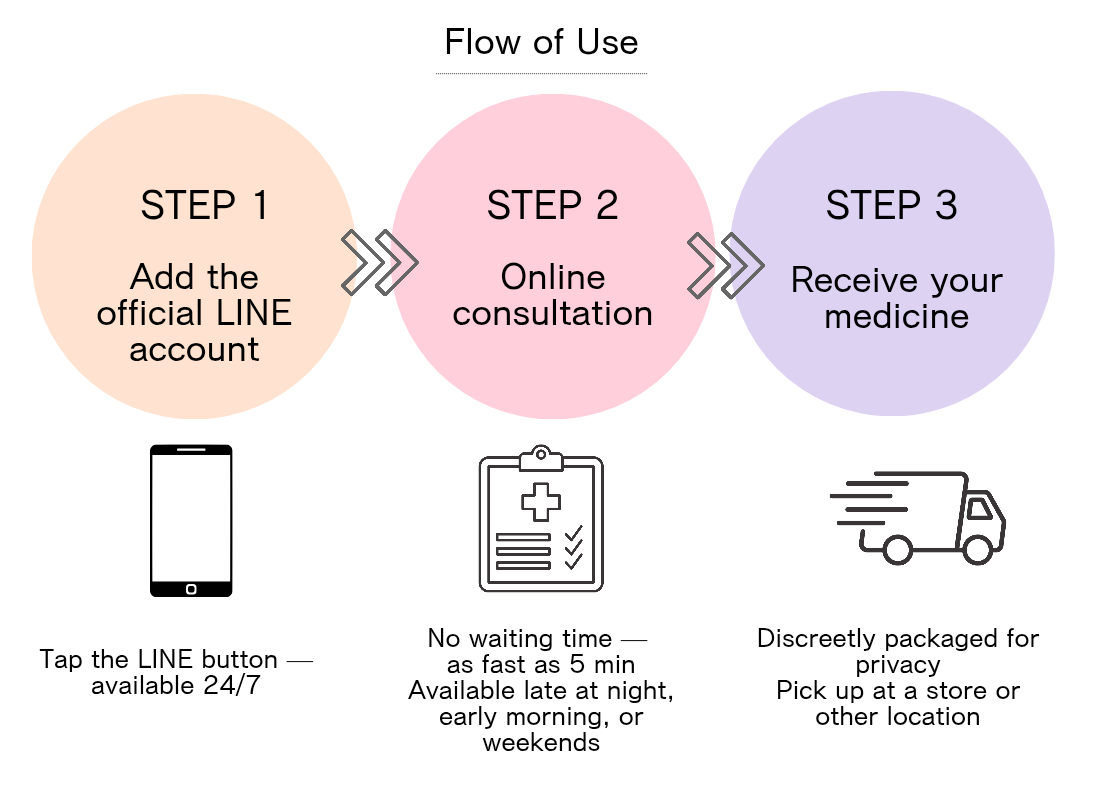
Personal Care Clinic can deliver emergency contraceptive pills in as little as 37 minutes. Prescription takes just 5 minutes! Applications submitted by 10:30 AM can be received the same day. (*Varies by area)This clinic is recommended for those who want to take the medication as soon as possible. Comprehensive aftercare following prescription ensures safe usage.
Understanding Planovar
(a combined oral contraceptive pill )and Menstrual Cycle Basics

To understand the relationship between Planovar(a combined oral contraceptive pill )and menstrual cycles, it’s essential to first grasp how these medications work and their effects on your body. The following sections provide detailed explanations:
- What are combined oral contraceptives? Hormone composition and mechanisms
- Understanding “withdrawal bleeding” timing after pill cessation
- Medical reasons for prescribing hormonal contraceptives
- Differences between high-dose and low-dose formulations
What Are Combined Oral Contraceptives? Hormone Composition and Mechanisms
“Aren’t these just contraceptive pills?” you might wonder.
Combined oral contraceptives are classified as hormonal medications containing two types of female hormones: estrogen (follicle-stimulating hormone) and progesterone (corpus luteum hormone). Higher-dose formulations contain more hormones than low-dose versions and are primarily prescribed for treating menstrual irregularities, cycle timing adjustments, and alleviating endometriosis-related pain.
These hormonal medications work by suppressing ovulation and artificially regulating hormonal balance to stabilize the endometrial lining. The standard regimen typically involves taking one pill daily for 21 days, followed by a 7-day hormone-free interval.
Understanding “Withdrawal Bleeding” Timing After Pill Cessation
“It’s been 2 days since I finished my pills, but my period hasn’t started yet. Is this concerning?”
During active pill consumption, your body receives artificial hormone supplementation. When you enter the hormone-free interval, the sudden drop in hormone levels causes the endometrial lining to shed, resulting in what’s called withdrawal bleeding. This represents your “medication-regulated menstrual period.”
Typically, bleeding begins 2-3 days after starting the hormone-free interval, though individual variation is common. Some women may experience bleeding as early as the first day of the break, while others might not see bleeding until the 5th day or later. First-time users or those with irregular lifestyle patterns may experience less predictable bleeding timing.
Medical Reasons for Prescribing Hormonal Contraceptives
“I have a wedding and overseas trip coming up, but my period might coincide with these events…”
Combined oral contraceptives are frequently prescribed for the following medical purposes:
1. Menstrual cycle timing: Adjusting menstrual timing for important events or travel
2. Dysmenorrhea: Managing severe menstrual pain and heavy bleeding
3. Endometriosis pain relief
4. Abnormal uterine bleeding control
For menstrual timing adjustments, the medication schedule and hormone-free intervals are tailored to match specific event dates. Under medical supervision, the standard protocol involves 21 days of active pills followed by a 7-day break, during which withdrawal bleeding (menstruation) occurs.
Learn more about how long it takes for your period to start after Planovar≫
Differences Between High-Dose and Low-Dose Formulations
“What’s the difference between different types of birth control pills? Are side effects more severe?”
The primary distinction between higher-dose and low-dose contraceptive pills is the hormone concentration. Higher-dose formulations compared to low-dose versions:
• Contain 2-3 times more hormones
• Are better suited for short-term treatment and cycle timing
• Provide contraceptive effects but aren’t exclusively for contraception
• Carry slightly higher side effect risks
Common side effects include nausea, headaches, and fluid retention. Additionally, women over 35 who smoke or have thrombosis risk factors may face increased blood clot risks, requiring careful medical consultation before use.
Low-dose formulations are designed for long-term use, minimizing side effect risks while maintaining hormonal balance. Higher-dose versions are better suited for short-term treatment but may have more pronounced bodily effects.
Learn more about nausea from Planovar >>
Main Causes of Delayed Periods and Pregnancy Possibilities

When your period doesn’t arrive after taking birth control pills, various causes are possible. Beyond pregnancy, factors related to your health condition and medication usage are also important. Here’s a detailed explanation:
- Six major non-pregnancy causes of missed periods (hormonal, dosage errors, etc.)
- Assessment criteria for no period after 1 week/10 days post-treatment
- Optimal timing for pregnancy tests and accuracy rates
- Special considerations during egg retrieval, IVF, and fertility treatments
Six Major Non-Pregnancy Causes of Missed Periods
“I’m not pregnant, but my period hasn’t come – is there something wrong with my body?!”
There are multiple reasons beyond pregnancy why periods may not arrive after birth control pill usage. Let’s examine the main six causes:
1. Individual variation: Time until withdrawal bleeding begins varies individually; some women may take 5-7 days
2. Dosage errors: Missed pills or significant timing variations disrupt hormonal balance
3. Stress: Severe stress affects hypothalamic function and disrupts hormone secretion
4. Extreme fatigue or sleep deprivation: Autonomic nervous system disruption affects hormonal balance
5. Rapid weight changes: Extreme dieting or excessive exercise suppresses hormone production
6. Drug interactions: Certain antibiotics or anticonvulsants may reduce pill effectiveness when combined
These causes are often temporary and frequently normalize with lifestyle improvements or in the next cycle. However, if similar symptoms persist repeatedly, medical consultation is recommended.
Assessment Criteria for No Period After 1 Week/10 Days
“It’s been 10 days and still no period… How long should I wait?”
Here are time-based assessment criteria for withdrawal bleeding timing after birth control pill completion:
3-5 days elapsed: Generally no concern. Most women begin withdrawal bleeding within this timeframe.
5-7 days elapsed: Still within normal range, but if concerned, consider using a home pregnancy test. Especially important if there was unprotected intercourse before pill usage with potential contraceptive failure.
7-10 days elapsed: Considered somewhat delayed. Take a pregnancy test and consider gynecological consultation if negative results still cause anxiety.
10+ days elapsed: May be medically classified as “amenorrhea.” Even with negative pregnancy test results, gynecological consultation is recommended to investigate underlying causes.
Remember these guidelines account for individual variation. First-time users may experience cycle instability while their body adjusts to the medication.
Optimal Pregnancy Test Timing and Accuracy Rates
“When should I use a pregnancy test for accurate results? Is first morning urine really better?”
Here’s information about pregnancy test reliability and optimal timing:
Pregnancy tests detect hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) hormone in urine. This hormone begins secreting after embryo implantation and increases daily.
Optimal testing timing:
• One week after expected period date (most reliable)
• 7-10 days after completing birth control pills
• 14+ days after intercourse (more reliable)
First morning urine (first urination after waking) has higher hCG concentration, providing higher detection rates. However, modern high-sensitivity tests can be used at any time.
Early pregnancy positive rates vary by elapsed time:
• Expected period date: approximately 75%
• One week after expected period: 95%+ accuracy
Even with negative results, false negatives are possible in early stages, so retesting after one week is recommended. For persistent anxiety, blood tests can detect pregnancy earlier, making gynecological consultation an option.
Special Considerations During Fertility Treatments
“I’m undergoing fertility treatment, but birth control pill effects make health management difficult…”
Special precautions apply when taking birth control pills during fertility treatments:
Post-egg retrieval:
Don’t take birth control pills without medical supervision due to OHSS (Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome) risk. Significant hormonal fluctuations may cause atypical reactions.
During IVF:
Follow treatment protocols precisely as pills affect embryo transfer timing and endometrial condition. Self-directed discontinuation or resumption impacts treatment effectiveness.
General fertility treatment:
• Pills may be actively used in certain treatment phases
• Post-pill menstrual patterns and basal body temperature records provide crucial treatment information – maintain detailed records
• Report any side effects or unusual symptoms to your physician immediately
Fertility treatment creates heightened hormonal sensitivity, making menstrual cycle variations more pronounced. Always consult your physician when in doubt.
Self-Assessment Guidelines and When to Seek Medical Care

When periods don’t arrive after birth control pill usage, appropriate action based on proper assessment criteria is crucial rather than self-diagnosis alone. The following sections detail self-assessment methods and optimal timing for medical consultation:
- 10-item checklist: Symptoms, duration, basal body temperature
- Age-specific considerations for suspected menopause/perimenopause
- Choosing between online consultation and gynecological office visits
- Emergency symptoms requiring immediate care (heavy bleeding, severe pain)
10-Item Self-Assessment Checklist
“What can I check myself? What should I pay attention to?”
When periods don’t arrive after birth control pill completion, check these 10 items:
1. Days elapsed: How many days since pill-free period began (7+ days warrants attention)
2. Compliance history: Any missed doses or timing irregularities
3. Basal body temperature: Continued elevated temperature (possible pregnancy indicator)
4. Pregnancy possibility: Unprotected intercourse before/after pill cessation
5. Physical changes: Nausea, fatigue, headaches, or other symptoms
6. Abdominal pain: Presence and severity of dull or sharp pain
7. Vaginal discharge: Changes in quantity or characteristics
8. Stress levels: Recent exposure to significant stress
9. Sleep patterns: Sleep deprivation or irregular sleep schedules
10. Weight changes: Rapid increases or decreases
Review these items carefully. If basal body temperature remains elevated for 10+ days or you experience pregnancy-like symptoms, consider using a pregnancy test or consulting healthcare providers.
Age-Specific Considerations for Menopause/Perimenopause
“I’m in my 40s – is this menopause-related or birth control pill side effects?”
Depending on age, post-pill menstrual irregularities might relate to menopausal symptoms. Here are age-specific assessment points:
Late 30s to Early 40s:
• Increasing menstrual cycle irregularities
• Menstrual flow changes Planovar(a combined oral contraceptive pill ) usage
• Increased hot flashes and sweating
These symptoms may indicate early menopausal symptoms (perimenopause). However, menopause in late 30s remains uncommon, so other causes should be considered.
Late 40s to 50s:
• Extreme menstrual interval extensions
• Minimal withdrawal bleeding after pill usage
• Pronounced hot flashes, night sweats, mood fluctuations
• Beginning bone density decline
This age group likely experiences perimenopausal/menopausal phases, with significantly varied pill effectiveness. Hormonal testing is recommended to assess current status.
For any age group, persistent absence of periods after pill usage warrants comprehensive examination including menopausal assessment to identify appropriate management strategies.
Choosing Between Online and In-Person Consultations
“Gynecology appointments are hard to book, and I’m too busy to visit…”
When seeking medical advice for post-pill menstrual irregularities, here’s a situation-based comparison between online and in-person consultations:
Online consultation appropriate for:
• Previous similar symptoms with physician-recommended monitoring
• Work/childcare obligations preventing weekday clinic visits
• Non-urgent situations requiring medical reassurance
• Regular contraceptive pill prescriptions
Online consultations offer easy booking and no waiting time while providing home-based consultation convenience.
In-person gynecological consultation required for:
• No period 10+ days after pill completion
• Severe abdominal pain or abnormal bleeding
• Positive or unclear pregnancy test results
• Symptoms requiring internal examination or ultrasound
These situations necessitate in-person examination with appropriate diagnostic testing.
Personal care Clinic offers hybrid care – initial online consultation with in-person referral when necessary. Choose the optimal method based on your schedule and circumstances.
Emergency Symptoms Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
“Should I go to the hospital immediately if these symptoms appear?”
Consider emergency medical consultation if you experience the following symptoms after birth control pill usage:
1. Heavy bleeding: Soaking multiple pads within 1-2 hours
2. Severe abdominal pain: Intense pain unresponsive to pain medication
3. Breathing difficulties or chest pain: Potentially dangerous symptoms indicating possible blood clots
4. Severe headaches with vision problems: Possible signs of hypertension or cerebrovascular issues
5. Fever above 101°F (38°C) with abdominal pain: Potential infection
6. Unilateral leg swelling or pain: Possible deep vein thrombosis
Estrogen in birth control pills can increase blood clot risk, making breathing difficulties, chest pain, and unilateral leg swelling particularly concerning. Seek emergency care immediately if these symptoms appear.
Smokers, women over 35, and those with family history of blood clots require heightened awareness of these symptoms. Never self-diagnose potentially life-threatening symptoms – seek prompt medical attention.
Case-Based Q&A: Common “No Period After Planovar(a combined oral contraceptive pill ) Pills” Concerns

Here are responses to frequently encountered “no period after birth control pill usage” concerns found online, based on real cases. We’ll provide detailed explanations covering common questions and expert responses:
- “Missed doses,” “hormone-free intervals,” “no period next month”… Real examples and responses
- Planovar(a combined oral contraceptive pill ) Pills usage after miscarriage or abortion
- Distinguishing from menopausal symptoms and additional testing
- Tips to avoid misinformation from social media and online forums
Real Cases: Missed Doses, Extended Breaks, and Ongoing Absence
“I’ve seen similar concerns online, but everyone seems worried… How does my case compare?”
Here are actual consultation cases with corresponding medical responses:
Case 1: Menstrual irregularity after missed doses
Q: “I missed taking my pills for 2 days, then resumed, but my period hasn’t come. Could I be pregnant?”
A: Missing pills for 2+ days can affect hormonal balance and disrupt withdrawal bleeding timing. If you had intercourse before or after the missed doses, pregnancy risk increases. We recommend pregnancy testing for confirmation.
Case 2: Extended hormone-free interval
Q: “I extended my hormone-free period to 10 days instead of 7. Will this affect my next cycle?”
A: Extended hormone-free periods increase the likelihood of ovulation occurring. Start your next pack as scheduled and use extra contraception for the first 7 days. Menstrual cycles may be disrupted but typically stabilize gradually in subsequent cycles.
Case 3: No period the following month
Q: “I had withdrawal bleeding after Planovar(a combined oral contraceptive pill ) Pills. but my natural period hasn’t come after a month”
A: After discontinuing birth control, your body may take 1-3 months to return to natural hormonal cycles. Stress and lifestyle disruptions also contribute. If periods don’t return after 3 months, gynecological consultation is recommended.
In all cases, when anxiety is significant, avoid self-diagnosis and consult medical professionals for the best approach.
Planovar(a combined oral contraceptive pill ) Pills Usage After Miscarriage or Abortion
“I was prescribed Planovar(a combined oral contraceptive pill ) Pills after miscarriage – when will my periods stabilize?”
Planovar(a combined oral contraceptive pill ) Pills usage after pregnancy loss requires special considerations:
Post-miscarriage usage:
After miscarriage, the body is prone to hormonal imbalances. Birth control pills during this period:
• Help endometrial recovery
• Usually started about 1 week after miscarriage procedures per physician instructions
• First 1-2 cycles may have unstable bleeding volume and duration
• Typically stabilize gradually after 2-3 cycles
Post-abortion usage:
Birth control after abortion helps endometrial repair and prevents immediate subsequent pregnancy:
• Often started immediately after the procedure
• Initial withdrawal bleeding may differ in volume and duration from normal
• Abnormal bleeding or severe pain may indicate procedure complications requiring prompt medical attention
Individual variation exists in returning to normal hormonal cycles. Seek medical consultation for concerning symptoms. Emotional care is equally important during this sensitive period, so prioritize rest and avoid overexertion.
Distinguishing Menopausal Symptoms and Additional Testing
“Are these birth control side effects or signs of menopause beginning?”
Post-pill symptoms can resemble menopausal symptoms. Here are distinguishing factors:
Characteristic menopausal symptoms:
• Hot flashes (sudden heat and sweating, especially upper body)
• Significant night sweats
• Severe mood swings (irritability, depression)
• Sexual discomfort or pain (vaginal dryness)
• Memory and concentration difficulties
• Multiple symptoms occurring simultaneously and persistently (months or longer)
Common birth control side effects:
• Temporary headaches or dizziness
• Nausea or breast tenderness
• Fluid retention
• Symptoms typically concentrated during or immediately after pill usage
Additional testing for menopause assessment includes:
1. Hormone testing: Measuring blood levels of FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) and estradiol
2. Transvaginal ultrasound: Assessing ovarian condition and follicle count
3. AMH (Anti-Müllerian Hormone) testing: Evaluating ovarian reserve
Comprehensive assessment of test results and symptoms helps determine menopausal progression. For women in their late 40s and beyond experiencing persistent symptoms, examination considering menopausal possibilities is recommended.
Avoiding Misinformation from Social Media and Online Forums
“I’ve researched online extensively, but everyone says different things – I’m so confused!”
Online information quality varies widely. Here are 5 key points for evaluating medical information:
1. Verify information sources
Prioritize information supervised by healthcare professionals like physicians or pharmacists, and official organizations like health departments or medical associations. Treat personal testimonials as reference only, never as sole decision-making factors.
2. Check publication dates
Medical information updates continuously. Verify information currency and avoid decisions based on outdated data. Current information is especially crucial for medication side effects and usage guidelines.
3. Beware of extreme language
Information using absolute terms like “always,” “never,” or “100%” without evidence requires caution. Medicine involves individual variation, and absolute solutions are rare.
4. Cross-reference multiple sources
Verify information across multiple reliable sources rather than relying on single sources. When information conflicts, prioritize more credible sources.
5. Recognize personal circumstance differences
Social media and forum information reflects specific poster circumstances. Remember that age, medical history, and life situations may differ significantly from yours.
Anxiety requires calm judgment. If online information increases anxiety, pause research and consult healthcare professionals for the most reliable solutions.
Self-Care and Lifestyle Practices When Periods Don’t Come
When periods don’t arrive after birth control pill usage, self-care alongside medical consultation is crucial. Here’s detailed guidance on self-care practices and lifestyle modifications to support hormonal balance and improve overall health:
- Stress management and optimizing sleep and nutrition
- How moderate exercise affects hormonal balance
- Are supplements and herbal medicines effective? Medical perspectives
- Pre-conception health screening recommendations
Stress Management and Optimizing Sleep and Nutrition
“I’m too busy for self-care – are there simple things I can do?”
Hormonal balance is significantly influenced by lifestyle factors, particularly stress, sleep, and nutrition:
Stress Management:
Stress affects the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis, contributing to menstrual irregularities. Simple stress reduction strategies include:
• Deep breathing: Practice abdominal breathing for 5 minutes, 3 times daily
• Mindfulness: Use meditation apps for 5-10 minute daily sessions
• Warm baths: Soak in 100-104°F (38-40°C) water for 20 minutes
Improving Sleep Quality:
Quality sleep regulates hormonal secretion rhythms:
• Avoid blue light 2 hours before bedtime
• Maintain consistent sleep and wake times
• Ensure 6-8 hours of adequate sleep
• Keep bedroom temperature between 60-66°F (16-19°C)
Hormone-Balancing Nutrition:
• High-quality protein: Eggs, poultry, fish, tofu
• Fiber: Helps eliminate excess estrogen
• Omega-3 fatty acids: Fatty fish, flaxseed oil, walnuts
• Phytoestrogens: Soy products and legumes
• Limit excessive caffeine, sugar, and alcohol consumption
Even with busy schedules, start with ensuring adequate sleep and eating proper breakfast. Small consistent changes contribute to hormonal stability over time.
How Moderate Exercise Affects Hormonal Balance
“I’ve heard exercise helps with periods, but what kind and how much should I do?”
Appropriate exercise helps balance female hormones and stabilize menstrual cycles. Here are specific exercise types and benefits:
Cardiovascular Exercise:
• Walking: 30 minutes, 3-5 times weekly
• Jogging: 20-30 minutes, 2-3 times weekly
• Swimming: 30 minutes, twice weekly
These activities improve circulation and reduce cortisol stress hormone levels. Avoid excessive intensity – maintain “conversational pace” as your guideline.
Yoga and Pilates:
Poses that enhance pelvic circulation are particularly effective:
• Child’s pose
• Butterfly pose
• Bridge pose
Practice 2-3 times weekly for 20-30 minutes each session.
Strength Training:
Light to moderate strength training improves insulin sensitivity and hormonal balance:
• Bodyweight exercises: Squats, ab exercises, push-ups
• Light dumbbell exercises
Aim for twice weekly, 20-30 minute sessions.
Important note: Excessive exercise (daily high-intensity training over 1 hour) can cause menstrual irregularities. Exercise causing rapid weight loss may negatively impact ovulation and menstruation.
During and after birth control usage, focus on balanced exercise combining moderate cardio with stretching rather than intense training.
Are Supplements and Herbal Medicines Effective? Medical Perspectives
“Do supplements and herbs actually work? What should I choose?”
Here are medical perspectives on supplements and herbal medicines for hormonal balance:
Female Hormone-Related Supplements:
• Vitex (Chasteberry): Some evidence for PMS symptom relief. Always consult physicians before combining with hormonal medications like birth control pills.
• Maca: Expected hormonal balancing effects, but scientific evidence is limited.
• Evening primrose oil: Sometimes used for PMS symptoms, but effectiveness varies individually.
• Folic acid: Essential for pregnancy planning, but limited direct effects on menstrual irregularities.
Herbal Medicines:
• Dang Gui Shao Yao San: Used for menstrual irregularities and pain from “cold” conditions
• Jia Wei Xiao Yao San: Effective for menstrual irregularities with irritability and anxiety
• Gui Zhi Fu Ling Wan: Expected to promote circulation and reduce pain
Herbal medicines should be prescribed based on individual constitution and symptoms. Consult physicians knowledgeable in herbal medicine rather than self-medicating.
Medical Perspectives:
Most gynecologists recommend using supplements and herbs as adjuncts to conventional medicine, with these important considerations:
• Potential interactions between hormonal medications and certain supplements
• Always consult physicians rather than self-medicating
• Significant individual variation in effectiveness
• Choose quality-assured products
Health supplements aren’t pharmaceuticals, so efficacy and safety aren’t fully guaranteed. Prioritize basic lifestyle improvements, considering supplements as supportive options only when symptoms persist.
Pre-Conception Health Screening Recommendations
“Is there anything I can do now to prepare for future pregnancy?”
For women planning future pregnancies, pre-conception health screening is highly recommended. This comprehensive health check can be done not only before marriage but whenever you begin considering pregnancy:
Pre-conception screening components:
1. Basic gynecological examination
• Cervical cancer screening
• Transvaginal ultrasound (checking for uterine fibroids, ovarian cysts)
• STD testing including chlamydia
2. Hormone testing
• AMH (Anti-Müllerian Hormone) testing for ovarian function
• Thyroid function tests
• Other reproductive hormone assessments
3. Infection and antibody testing
• Rubella antibody testing
• Hepatitis B and C testing
• HIV testing (optional)
4. General health assessment
• Blood tests (anemia, blood glucose levels)
• Blood pressure monitoring
• Urine analysis
Optimal timing:
Ideally, allow a 3-6 month preparation period between considering pregnancy and actively trying to conceive. This timeframe ensures adequate time for treatment and lifestyle improvements if issues are identified.
For example, low rubella antibody levels require vaccination, but pregnancy must be avoided for 2 months post-vaccination. Additionally, folic acid supplementation is recommended at least 1 month before conception.
When planning pregnancy after birth control usage, it’s generally recommended to wait 1-3 months after completion for natural menstrual cycles to resume. Completing pre-conception screening during this interval helps ensure smooth conception and healthy pregnancy preparation.
Medication Management and Alternative Pill Comparisons

Learn effective birth control pill management strategies and alternative options to reduce menstrual irregularity risks. Choosing appropriate management methods and medications helps prevent complications and achieve more stable cycles:
- Preventing missed doses with apps and calendar systems
- Differences between 7-day, 10-day, and 14-day regimens
- Pros and cons of medium-dose vs. low-dose pills
- Ensuring continuity through prescription delivery services
Preventing Missed Doses with Apps and Calendar Systems
“I’m busy and sometimes forget to take my pills – are there better methods?”
To maximize birth control effectiveness, here are missed dose prevention techniques:
Specialized app usage:
Pill management apps offer multiple convenient features:
• Alarm functions: Daily notifications at consistent times
• Dosage tracking: Record taken/missed doses
• Missed dose guidance: Step-by-step instructions for catch-up
• Prescription reminders: Alerts for refill dates
Recommended apps: “Pill Reminder,” “MyPill,” “Clue”
Daily routine integration:
• Take pills at consistent times (after breakfast, dinner)
• Link with daily habits like tooth brushing
• Keep pills in visible locations (vanity, desk)
• Use weekly pill organizers for visual confirmation
Backup strategies:
• Partner reminders as additional support
• Portable cases for travel and outings
• Backup packs at work or family homes
• Calendar notes for travel: “bring pills”
If doses are missed, take immediately upon remembering and continue normally. For 24+ hour delays or consecutive missed doses, consult your prescribing physician.
Differences Between 7-, 10-, and 14-Day Planovar Courses
“My doctor told me to take it for 14 days—what’s the difference?”
The duration of a Planovar course varies by purpose. Common options are 7 days, 10 days, and 14 days. Here are the key differences:
7-Day Course
- Shortest regimen.
- Mainly for short-term period shifting.
- Begin a few days before the event; stop after the event.
- Relatively lighter hormonal impact.
- Lower risk of side effects.
- Withdrawal bleeding usually occurs 2–4 days after the last pill.
10-Day Course
- Medium-length regimen.
- For delaying the period by about one week.
- More stable withdrawal bleeding than shorter courses.
- Also used to ease endometriosis or dysmenorrhea symptoms.
- Withdrawal bleeding typically 2–5 days after the last pill.
14-Day Course
- Longest regimen.
- For adjusting the period by around two weeks or for therapeutic aims.
- Used for endometriosis, severe menstrual pain, or controlling breakthrough bleeding.
- Side effects may be more likely due to longer exposure.
- Withdrawal bleeding usually 3–5 days after the last pill.
In general, longer courses mean greater hormonal exposure, which can increase the likelihood of side effects. Longer courses may also slightly delay the onset of withdrawal bleeding or increase the amount of bleeding.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions. Changing the course length on your own can cause unexpected bleeding or, conversely, delayed/absent periods. Your physician will determine the optimal duration based on your goals and health profile.
Medium-Dose vs. Low-Dose Pills: Pros and Cons
“Should I use Planovar or a low-dose pill? What’s the difference?”
Medium-Dose Pills (e.g., Planovar) — Advantages
- Fast relief for menstrual pain and heavy bleeding.
- Strong effect on endometriosis-related pain.
- Suitable for short-term period shifting.
- High bleeding-control efficacy.
- Generally more affordable (about ¥1,000–¥2,000 per pack).
Medium-Dose Pills — Drawbacks
- Side effects (nausea, headache, etc.) may be more frequent than with low-dose pills.
- Slightly higher risk of thrombosis compared with low-dose pills.
- Not ideal for long-term continuous use.
- May trigger acne/skin issues in some people.
Low-Dose Pills (e.g., Triquilar, Marvelon) — Advantages
- Fewer side effects on average.
- Appropriate for long-term use.
- Some formulations can improve acne/skin.
- Potential improvement in PMS/PMDD symptoms.
- High contraceptive efficacy (>99% with correct use).
Low-Dose Pills — Drawbacks
- Benefits may take 2–3 cycles to appear.
- Typically more expensive (about ¥2,000–¥3,000 per pack).
- Breakthrough bleeding is common early on.
- Requires same-time daily dosing.
How to Choose
- Short-term period shifting / temporary treatment → Consider a medium-dose pill.
- Long-term hormone management / contraception → Consider a low-dose pill.
- Worried about side effects → A low-dose pill may be preferable.
- Need fast effect → A medium-dose pill may work quicker.
Both medications require a prescription. Discuss your lifestyle, medical history, and goals with your doctor to choose the best option. Even among low-dose pills, hormone types and ratios vary, allowing selection tailored to your individual needs.
How to Stay Consistent: Subscription Delivery
“Going to the gynecologist every time is tough—how can I keep this up more easily?”
If you take hormones continuously, a telemedicine + subscription delivery model can reduce the hassle of clinic visits and improve adherence.
Benefits of Telemedicine + Subscription
- Save time: convenient for busy schedules (work, childcare).
- Prevent running out: the next pack ships automatically.
- Privacy: discreet consultations and delivery.
- Consistent dosing: fewer gaps make it easier to continue.
- No appointments needed: avoid crowded waiting rooms.
How It Works
- Initial evaluation: many clinics require an in-person visit first.
- Switch to online care: if appropriate, enroll after consulting your physician.
- Set up your subscription:
- Choose delivery frequency (e.g., monthly or every 3 months).
- Register a payment method.
- Specify your delivery address.
- Regular follow-ups: online check-ins every 3–6 months.
- Adjust as needed: modify medication or schedule based on side effects or health changes.
How to Choose a Trusted Service
- Qualified clinicians: availability of OB/GYN specialists.
- Emergency support: clear channels for side-effect concerns.
- Transparent pricing: clearly listed consultation, medication, and shipping fees.
- Flexible policies: easy pause/cancellation options.
- Data security: robust protection of personal and medical information.
At Personal Care Clinic, OB/GYN-led online consultations can be combined with a medication subscription service. Your first visit includes thorough counseling to match your lifestyle with the right pill and schedule. With regular follow-ups, we support safe, confident continuation through consistent communication with your doctor.
Conclusion

This comprehensive guide has examined the medical causes and management strategies for absent periods after birth control pill usage. Here are the key takeaways:
• Combined oral contraceptives contain hormones that typically cause withdrawal bleeding during hormone-free intervals
• Beyond pregnancy, causes include individual variation, stress, dosage errors, and drug interactions
• Consider pregnancy testing after 5-7 days without bleeding; seek gynecological consultation after 10+ days
• Apps and calendars effectively prevent missed doses
• Stress management, quality sleep, and balanced nutrition support menstrual cycle stability
• Medium-dose and low-dose pills each offer distinct advantages suited to different purposes
When experiencing concerning symptoms, avoid self-diagnosis and consult healthcare professionals for the most reliable guidance. The following detailed topics address common concerns:
- Six major non-pregnancy causes of missed periods
- Assessment criteria for no period after 1 week/10 days
- Optimal pregnancy test timing and accuracy rates
- 10-item self-assessment checklist
Menstrual cycles serve as important indicators of women’s health. Hormonal imbalances can cause various health issues, making regular gynecological care and accurate knowledge essential.
Personal care Clinic supports women experiencing menstrual irregularities and hormonal imbalances through flexible care including online consultations. From birth control prescriptions to menstrual cycle management and future pregnancy planning, we provide personalized support tailored to individual circumstances. Please consult us if you have concerns.





